Ultrasound and X-ray hysterosalpingography. What is hysterosalpingography? echo hsg consequences
The fallopian tubes connect the ovary to the uterus, and the mature egg, moving from the ovary, is fertilized by the sperm in the tube. The tube then pushes the egg into the uterus. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes is one of the causes of female infertility.
Obstruction may be due to:
- operations on the pelvic organs (including removal of appendicitis);
- transferred inflammation (most often - chlamydia).
Obstruction can occur not only in the tube itself, but also between the ovary and the tube as an adhesion (adhesion of the walls of the fallopian tubes and ovaries).
Fallopian tube adhesion
Is it necessary to remove the fallopian tubes in case of their obstruction?
- Conservative treatment (no surgery) used in cases where obstruction is caused by inflammatory processes. At the same time, anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy are prescribed, but in the case of the formation of adhesions, such treatment is ineffective.
- Surgical treatment- surgical intervention. Usually, surgical treatment is carried out by laparoscopy - it practically does not give complications. But no one can give a 100% chance of curing infertility associated with impaired patency of the fallopian tubes. Removal of the fallopian tubes is an extreme measure, and is used in exceptional cases.
How to check the patency of the fallopian tubes?
Checking the patency of the fallopian tubes can be carried out in several ways:
- diagnostic laparoscopy (checking the patency of the fallopian tubes is carried out, as a rule, during the operation to remove adhesions - laparoscopy is usually not prescribed just to check the tubes);
- HSG (hysterosalpingography, MSG, metrosalpingography - other names);
- hydrosonography (ultrasound);
- fertiloscopy (a method similar to laparoscopy; often combined with it). The difference between fertiloscopy and laparoscopy is that the instruments are inserted not through the abdominal wall, but through the vagina.
How to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, which method to choose?
Taking into account the fact that both laparoscopy and fertiloscopy are traumatic methods, and ultrasound does not give a clear “picture of what is happening”, HSG is the optimal method in most cases.
HSG, or hysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) - X-ray examination of the fallopian tubes for patency. Hysterosalpingography is an important stage in the examination of a woman diagnosed with infertility. The accuracy of the study is at least 80%.
Hysterosalpingography allows you to diagnose:
- patency of the fallopian tubes;
- the state of the uterine cavity and the presence of endometrial pathology - an endometrial polyp;
- the presence of deformities in the development of internal organs and the uterus, for example, a saddle uterus, an intrauterine septum, a bicornuate uterus, etc.
How is tubal patency checked with HSG?
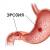
A contrast agent is injected into the cervix - a blue solution. It fills the uterine cavity and enters the tubes, from which it flows into the abdominal cavity. In this case, an x-ray is taken, which shows the state of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes.
In most cases, the procedure helps not only to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes, but also makes it possible to see the presence of tube deformation:
- extension;
- tortuosity;
- braces, etc.
Hysterosalpingography can be performed only in the absence of inflammation. Before the start of the examination, they are tested for HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, as well as a general smear for the flora. HSG does not require general anesthesia.
As a rule, in women who are trying to become pregnant, hysterosalpingography is performed on the 5th-9th day of the menstrual cycle, if its duration is 28 days. If a woman is protected from pregnancy, the examination is possible on any day of the cycle, except for menstruation.
Disadvantages of hysterosalpingography
- The procedure is rather unpleasant.
- The pelvic organs are irradiated.
- After HSG during one menstrual cycle it is necessary to be protected.
Hysterosalpingography
Ultrasound of the patency of the fallopian tubes
Testing for patency of the fallopian tubes Ultrasound (hydrosonography) is an alternative to hysterosalpingography. Ultrasound has several advantages over HSG:
- less unpleasant procedure;
- unlike HSG, no radiation is used, which can have a negative impact on a woman's reproductive health;
- while careful protection is required after HSG, tubal ultrasonography is safe.
The main drawback of the procedure is the lower accuracy of the results compared to the HSG.
When is the patency of the ultrasound tubes checked?
An ultrasound tube test is usually performed on the eve of ovulation: at this time, the likelihood of spasm is reduced and the cervical canal is dilated. Unlike hysterosalpingography, in this case it is not very important on which day of the cycle the tubes are checked for patency using an ultrasound scanner. Before checking the patency of the fallopian tubes, it is necessary to take tests to exclude the presence of inflammatory diseases.
How is the patency of the fallopian tubes checked by ultrasound?
Determining by ultrasound the patency of the fallopian tubes is almost painless. A special catheter is inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity, warm saline is slowly poured into it under ultrasound control. If it flows into the fallopian tubes, then the tubes are passable. If not, their obstruction is likely.
Disadvantages of checking the patency of the fallopian tubes by ultrasound:
- relatively large amounts of fluid, as well as spasms of the uterus and fallopian tubes, discomfort can be caused;
- if the ultrasound showed that saline does not pass, this may not always mean obstruction of the tubes. The reason for this may be a strong spasm.
Laparoscopy. How to check the patency of the fallopian tubes with its help?
Laparoscopy is a surgical method for assessing the patency of the fallopian tubes. Through punctures in the abdominal wall with the help of optical instruments, an examination of the internal organs is carried out. If you are scheduled for laparoscopy, the forum can help you choose a clinic or even a surgeon.
Laparoscopy in gynecology is a method for the treatment and diagnosis of various pathologies of the pelvic organs. Operation laparoscopy is one of the modern methods of surgery with minimal intervention and damage to the skin. Laparoscopies are performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Laparoscopy can be performed to clarify various diagnoses. If you feel pain after laparoscopy, contact the clinic where you had the operation.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is an operative research technology in which the doctor examines the abdominal organs without making large incisions on the abdominal wall. Most often, two small incisions are made. A small amount of gas is injected into the abdominal cavity to increase the field of view.
A device called a laparoscope is inserted into one incision - a thin tube at one end with a lens, and at the other with an eyepiece (the second end can also be connected to a video camera unit that transmits an image to the screen). A manipulator is inserted into another incision, with the help of which the doctor displaces the abdominal organs, carefully examines them and makes a diagnosis.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed to assess the condition of the outer surface of the fallopian tubes and pelvic organs, as well as to identify their pathologies.
The most common operations:
- laparoscopy of the ovaries;
- laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes;
- laparoscopy of the abdominal organs.
After laparoscopy:
- The patient stays at the hospital, as a rule, for no more than a day: doctors monitor her condition, perform an ultrasound scan. After 2-3 days you can return to work.
- It is not recommended to drink alcohol and heavy food in the next 2-3 weeks after the operation. - Sex should be postponed for 2-3 weeks to avoid infection.
- Physical activity should be increased evenly. It is better to start with walking and gradually increase their duration. Heavy after the operation should not be lifted.
Laparoscopy of the ovaries
This procedure is performed not only to remove cysts. At the same time, this is the most effective method of treating ovarian cysts of a different nature. It can also be an effective treatment for endometriosis, a disease in which cells from the inner layer of the uterine wall grow outside of this layer. In this case, an endometrioid cyst may form.
Laparoscopy of the ovaries allows you to remove the cyst and adhesions, return the woman the opportunity to have children. Literally a couple of days after the laparoscopy of the ovarian cyst was performed, he returns to his normal boundaries and fully restores his functions.
Pain after laparoscopy is very rare, the stitches usually heal quickly without causing discomfort - painkillers are taken in extreme cases, as directed by a doctor.
Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is not an easy operation. Choose a good doctor, because often the appearance of cysts in the future, as well as the possibility of pregnancy, depends on the accuracy of the operation.
Laparoscopy of the uterus
Laparoscopy of the uterus is an effective way to treat fibroids. The operation is also prescribed for the treatment of various malformations of the uterus.
Laparoscopy of uterine fibroids
The determining factors in choosing a method for treating uterine fibroids are the intention to have children in the future, the size of the uterus, the size of the myoma nodes, and their location. Laparoscopy is a good option for removing small fibroids.
Laparoscopy of uterine fibroids is not performed in such cases:
- the size of the uterus is larger than the fetus at the 11-12th week of pregnancy;
- multiple myomatous nodes developed;
- the size of the nodes is large;
- myoma nodes are located low.
In these cases, it is better to use other methods of removal, such as laparotomy.
Treatment of fallopian tubes with laparoscopy
Tubal laparoscopy is a method in which anesthesia is used, and the occurrence of spasm is excluded. Therefore, checking the tubes using laparoscopy gives very accurate results. Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes allows you to remove adhesions. The operation of laparoscopy is prescribed if treatment of the fallopian tubes and their pathologies is necessary.
Laparoscopy of the tubes may be prescribed in the following cases:
- formation of adhesions of the fallopian tubes;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- diagnosis of female infertility;
- endometriosis;
Period after laparoscopy
If menstruation is painful, then the first menstruation after laparoscopy usually passes with more blood loss than usual and longer duration. This is because internal organs take longer to heal than incisions in the abdominal wall. In this regard, the first menstruation is usually more painful. But still, with a strong menstrual pain should consult a doctor.
Pregnancy after laparoscopy
After laparoscopy is done, you can become pregnant within a few months, but immediately after the operation for 2-3 weeks, you must completely abandon sexual intercourse. After that, you can plan conception. Pregnancy after laparoscopy is quite possible in the near future.
Women who have become pregnant after laparoscopy within a few months are observed by a gynecologist. Often pregnancy is accompanied by drug treatment, a woman takes drugs to support the normal hormonal background of pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur after laparoscopy, this operation can be repeated several times.
Laparoscopy - reviews
If you are scheduled for laparoscopy, the forum is not the best source of information. It can come in handy in one case: if you want to choose a clinic or a doctor: patients who have had laparoscopy leave reviews very willingly.
Is it worth restoring the patency of the pipes?
You can get pregnant within about a year after the restoration of the patency of the tubes - the likelihood that they will soon become impassable again is very high. In addition, the tube should not just be passable: it should move the fertilized egg to the uterus. If she does not do this, an ectopic pregnancy is formed.
Any operation to restore tubal patency increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy. Thus, the restoration of patency is far from a guarantee that you will be able to get pregnant. In addition, any operation can start the process of adhesion formation.
If you are young and there are no more factors that prevent you from getting pregnant, it makes sense to operate the tubes. If you are over 35 and have been trying to have a baby for a long time, consider artificial insemination. With each ovulation, the "quality" of the eggs deteriorates, and you should not waste months on the restoration of the tubes - time is against you. Based on everything that we have described above, consult with your doctor to find out if you should even deal with the restoration of tubal patency.
One common cause of infertility is blocked fallopian tubes. There are several ways to diagnose this condition. However, the most used of them is the consequences of which are not very pleasant, but quite tolerable.
This study can be carried out on different days of the menstrual cycle as prescribed by the doctor. On the eve of the evening you can not eat up, on the day of the study, eat and drink. Before the HSG, it is necessary to give an enema, empty the bladder and shave off the pubic hair.
HSG, the consequences of which can be minimized by passing the necessary examination before it, is usually performed without anesthesia, however, if the patient wishes, light anesthesia can be used. A week before the study, you need to take urine and blood tests, make swabs from the vagina and check for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis.
One of the most unpleasant, but possible consequences of HSG, is the inflammatory process. Therefore, after the procedure, you need to carefully consider your health. Temperature, pain and after HSG for more than three days - a reason to consult a gynecologist.
It is impossible to conduct a study in the presence of an inflammatory process in the genital tract or if it has recently been transferred. Exacerbation of a general disease is a contraindication to the procedure (pyelonephritis, influenza, pneumonia).
The radiopaque substance can cause allergies. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the reaction to the drug used, as a rule, it contains iodine.
In a cycle in which HSG is performed, the consequences of which can be pleasant, it is imperative to protect yourself, even if pregnancy has not occurred for a long time. This is due to the fact that after the study, the likelihood of its onset increases significantly due to the flushing effect.
A contrast agent injected into the tubes eliminates small adhesions that previously prevented the onset of conception. This is indeed an established fact, which is why many women have high hopes for this procedure.
HSG, the results of which are of great value for finding out the causes of infertility, is carried out in the X-ray room on a special chair. After a two-handed examination, several pictures are inserted into the uterus and taken.
This procedure is tolerated by patients in different ways. Some note only discomfort, others complain of a sharp soreness. Most likely this is due to the threshold of sensitivity, which is individual for each person.
After the HSG, light bleeding is possible, so it is necessary to bring a sanitary napkin with you. It usually goes away after a couple of hours.
After the study, there are painful sensations resembling the onset of menstruation. They are especially pronounced in a sitting position. A slight rise in temperature and not abundant is also possible. These phenomena are the norm in the first few days.
As a result of the HSG, the patient receives images in her hands, which can be used to see if they are passable and if not, in which department. In addition, they can be used to diagnose diseases such as endometriosis, tuberculosis of the reproductive system, various pathologies, including congenital (bicorn, saddle).
It is important to remember that in 20% of cases, HSG gives a false diagnosis of tubal obstruction. This can happen if a woman has them long and narrow. Then the contrast agent simply does not have time to get into the abdominal cavity.
In addition, due to stress and anxiety, spasm of the tubes can occur. Therefore, it is imperative to drink no-shpu before the study. To prevent the inflammatory process, the doctor may prescribe a course of suppositories, tampons or antibiotics.
Thus, HSG, the consequences of which can be both negative (inflammation) and positive (long-awaited pregnancy), is a very informative procedure. It allows you to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, to detect their pathology, as well as the uterus. To prevent negative consequences, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the gynecologist.
This method of studying the condition of the adnexal tubes and the uterine body in the medical language is called hysterosalpingography(from hystera - uterus (Greek) and salpinx - fallopian tube (Greek)).
The whole examination process consists in the fact that the body of the uterus and the lumen of the fallopian tubes are filled with a contrast solution, which is delivered to the body through a catheter through the vaginal passage.
After that, using such devices as: x-ray or, the gynecologist examines the state of the reproductive sphere (the contrast solution makes it possible to determine all kinds of neoplasms, adhesions, local pathological phenomena, etc.), in addition, the method allows you to determine whether the contrast passes through the tubes of the uterus to the area peritoneum.
If it passes, then the patency of the processes of the uterus without pathologies, their lumen is unobstructed.
In medical practice, there are two types of HSG - using an X-ray machine and echohysterosalpingoscopy (echo-HSG of the fallopian tubes):
- When operating X-ray equipment the contrast is introduced gradually, in small volumes, and the gynecologist takes a number of images one after the other.
- During ultrasound examination, saline solution is introduced into the uterine cavity, which performs an auxiliary therapeutic effect, for example, revealing minor adhesions. Largely due to this, after HSG ultrasound, the desired conception and pregnancy often occur, in the case when the difficulty was only in the presence of simple pathologies.
Hysterosalpingography- This is a medical manipulation that is performed to study the structure and content of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes and the presence of a lumen in the tubes.
Basically, gynecologists use hysterosalpingography to monitor the condition of the reproductive organs in such representatives of the female population who cannot become pregnant or who have previously undergone several episodes of involuntary abortion (miscarriages).
Indications for carrying out
The most important purpose of the hysterosalpingography procedure is to make an accurate diagnosis and get rid of a woman's infertility.
 At the time of the GHA, the following is established:
At the time of the GHA, the following is established:
- Pipe permeability and the definition of the lumen, their structure is the main task of the study;
- Identification of any abnormalities in the uterine body, including anomalies of its structure (bicornuate, saddle-shaped uterus, the presence of a septum);
- Neoplasms, cysts, organs of the genitourinary and reproductive spheres.
In circumstances where a couple does not conceive within one year, or at much longer periods, hysterosalpingography becomes the most initial examination recommended by every gynecologist.
The absence of a lumen of the fallopian tubes occurs due to previously transferred sexually transmitted diseases, inflammation, congenital abnormalities. Hysterosalpingography also helps the gynecologist to assess the physical condition of the uterine body.
Contraindications

Checking the patency of the fallopian tubes
There are three ways in which .
The main one is hysterosalpingography. This study consists in x-ray - the study of the fallopian tubes.
At the beginning, a rubberized tip is introduced inside the uterine cervix, and with its help a thin rod called a cannula. A dye solution (blue) is injected through the cannula into the cavity.
After that, a picture is taken by means of the exploitation of X-rays. Which displays the general condition of the uterine body and tubes.
Other ways to study the reproductive sphere include:
- Sonohysterosalpingography(similar methods are echohysterosalpingography, sono-, echo-, hydrosonography). This is a method with not so pronounced pain sensations as with HSG of the uterine tubes. The method is carried out by introducing a warm saline solution into the cavity of the uterine cervix using a catheter, and then visually examining the penetration of the solution through the ultrasound machine.
 .
As for diagnostic laparoscopy, this is the most inhumane and traumatic method for studying problems in the fallopian tubes. Almost always associated with getting rid of adhesions, and for this reason is not performed only for verification. It is carried out by performing a puncture of the abdominal tissues in order to introduce a special tool that makes it possible to visually study the organs and tissues of the reproductive system. Carrying out laparoscopy or blowing the tubes of the uterus. It is used when a woman has an allergic perception to the contrast component. It is carried out by artificially creating air pressure in the uterus, through a soft tube and a pressure gauge.
.
As for diagnostic laparoscopy, this is the most inhumane and traumatic method for studying problems in the fallopian tubes. Almost always associated with getting rid of adhesions, and for this reason is not performed only for verification. It is carried out by performing a puncture of the abdominal tissues in order to introduce a special tool that makes it possible to visually study the organs and tissues of the reproductive system. Carrying out laparoscopy or blowing the tubes of the uterus. It is used when a woman has an allergic perception to the contrast component. It is carried out by artificially creating air pressure in the uterus, through a soft tube and a pressure gauge. Ultrasound diagnostics, which makes it possible to accurately determine the state of the body of the uterus and the permeability of the fallopian tubes. Today, this method often becomes the initial stage in establishing the tubal root cause of infertility, since ultrasound hysterosalpingography is characterized by a fairly good percentage of information, along with HSG using X-rays (80-91%), and in addition, it is acceptable in terms of pain and less invasive event. Ehogisterosalpingography is performed under stationary conditions, in the initial phase of the menstrual cycle (when menstruation passes). A gynecological catheter is inserted inside the uterine cavity, after which a contrast solution of about 10 to 20 ml is introduced. (saline solution, liquid glucose, furatsilin, echovist, levovist, etc.). The substance being in the cavity provides a visual inspection of the uterine body and makes it possible to give a much more definite assessment of the features of its structure. The subsequent introduction of contrast implies its penetration into the tubes, and then into the abdominal location, which may indicate the presence of a lumen and patency of the tubes. If there is an impermeability of the fallopian tubes, the introduced fluid is not able to penetrate into the abdominal cavity, or accumulates in the tubes. A distinctive feature of ultrasonic HSG is its auxiliary therapeutic effect. The fluid injection formed during the procedure destroys minor adhesions in the pipes, thereby ensuring their permeability. Due to this, conception after HSG of the fallopian tubes becomes a very common result.
Ultrasound diagnostics, which makes it possible to accurately determine the state of the body of the uterus and the permeability of the fallopian tubes. Today, this method often becomes the initial stage in establishing the tubal root cause of infertility, since ultrasound hysterosalpingography is characterized by a fairly good percentage of information, along with HSG using X-rays (80-91%), and in addition, it is acceptable in terms of pain and less invasive event. Ehogisterosalpingography is performed under stationary conditions, in the initial phase of the menstrual cycle (when menstruation passes). A gynecological catheter is inserted inside the uterine cavity, after which a contrast solution of about 10 to 20 ml is introduced. (saline solution, liquid glucose, furatsilin, echovist, levovist, etc.). The substance being in the cavity provides a visual inspection of the uterine body and makes it possible to give a much more definite assessment of the features of its structure. The subsequent introduction of contrast implies its penetration into the tubes, and then into the abdominal location, which may indicate the presence of a lumen and patency of the tubes. If there is an impermeability of the fallopian tubes, the introduced fluid is not able to penetrate into the abdominal cavity, or accumulates in the tubes. A distinctive feature of ultrasonic HSG is its auxiliary therapeutic effect. The fluid injection formed during the procedure destroys minor adhesions in the pipes, thereby ensuring their permeability. Due to this, conception after HSG of the fallopian tubes becomes a very common result.- x-ray The peculiarity of this method of study is that a woman is injected with contrast into the uterine cavity through the thinnest tube. In the current realities for HSG of the fallopian tubes, only such components are used that dissolve in water: verografin, urotrast, cardiotrast. They have no side effect and are absolutely harmless to the mucous membranes of all organs of the reproductive system. After that, 3 X-ray photographs are taken:

HSG of the fallopian tubes under x-ray fixation lasts about 40 minutes. In the total volume during this time of the examination, 10-20 ml of contrast fluid is infused.
Through X-rays or HSG, the fallopian tubes are studied exclusively in women who are not in a state of pregnancy, since radiation is always harmful to the embryo. In such circumstances, other possible methods are used, i.e. echography.
An X-ray examination can provide more information, and it is much easier to assess the existing picture of the state of the organs of the reproductive function.
However, the analysis also has some disadvantages. They are expressed in: irradiation, albeit in a very small dose; probable allergic manifestations on the contrast liquid; physical violations of the integrity of the surface of tissues, leading to bleeding.
How is the patency of the fallopian tubes checked?
 At the time of the HSG, the patient is placed on the couch. When the procedure is carried out using an x-ray, the equipment is located above it.
At the time of the HSG, the patient is placed on the couch. When the procedure is carried out using an x-ray, the equipment is located above it.
When an ultrasound is performed, the specialist uses a vaginal sensor.
Until the introduction of the catheter, the doctor applies an antiseptic to the vulva, vagina and cervix.
As usual, HSG is performed without pain, however, a woman will still have to feel minor inconvenience: during the introduction of the tube into the vaginal cavity and during the achievement of fluid pressure.
The pain feeling is very similar to the pulling manifestations in the initial days of menstruation. The examination is more difficult for nulliparous patients, since their uterine cervix is still dense, possibly obstructing the introduction of the catheter.

Analyzes for HSG
Prior to the time of the study, it is required to provide biomaterials (blood, urine) for analysis and in addition. If pathogenic microorganisms are present, the implementation of HSG can be dangerous, since the disease can "rise" inside the uterine body.
Preparation for the GHA
 Hysterosalpingography is best done in the first part of the cycle, preferably in the initial few days, immediately after the end of menstruation.
Hysterosalpingography is best done in the first part of the cycle, preferably in the initial few days, immediately after the end of menstruation.
At this time, the uterus is still very thin, the uterine cervix is more pliable, for this reason the gynecologist has a greater overview and the introduction of a fluid supply device is not difficult.
For this procedure, vaginal discharge must be completed without fail, otherwise blood clots can change the image seen by a specialist.
Preparatory actions for the HSG of the fallopian tubes are related to the method by which the test will be performed.
HSG with x-ray
This examination is performed in the first part of the cycle of critical days, while the endometrium is quite thin and does not change the visual image. The most suitable time is the interval between the first "clean" days immediately after menstruation and ovulation. With a 28-day cycle, this is 6-12 days.
When the referral for the HSG is issued in advance, the woman is informed that from the time of the first bleeding until the day of the study, restrictions on sexual contacts (their exclusion) are required.
 For the procedure, the patient needs to prepare and pass the following tests:
For the procedure, the patient needs to prepare and pass the following tests:
- General blood analysis;
- Blood for diseases such as AIDS, jaundice, gonorrhea.
- In addition, a general urine test is provided, and the level of cleanliness of the vaginal cavity is determined.
On the eve of the morning when the study is performed, it is required to do an enema and empty the intestines through Fortrans.
On the day of the HSG, you need to wash yourself very cleanly, shave off your pubic hair. The survey is carried out in the morning. You can’t eat anything, you are allowed to drink no more than 1 glass of water 1.5 hours before the analysis.
Preparation for the HSG of the fallopian tubes right before the procedure, consists in the fact that the woman empties the bladder and removes all metal objects and clothing that enters the area of the x-ray image.
Consequences and complications
The aggravation of the condition during the HSG of the fallopian tubes is very rare.
The most important of which are:

So, we can say that side effects from HSG of the fallopian tubes are associated, firstly, with careful preparation for the procedure - the establishment of all negative indications.
Even the harmlessness of the HSG procedure cannot promise the absence of difficulties and consequences:
- The initial line in this list may be an allergic manifestation to contrast components. This occurrence is typical for women who have previously had similar "answers" on other tests. An allergic reaction may also appear in women with severe diseases of the respiratory system (asthma, tuberculosis).
- Bleeding, disease or damage to the uterus is still infrequently observed.
An x-ray examination does not pose any threat to the patient at all, since its dose is 0.4-5.5 mGy, which is much lower than that which could lead to a violation of the epithelium.
Research results
On x-ray images, if there are no adhesions, the outline of the uterus filled with solution, thin tube ducts and contrast flowing into the abdominal location are clearly visible. With such a picture, a specialist can talk about the permeability of the fallopian tubes.
However, when the liquid stops on any fragment of the pipe, accordingly, there is an assumption about its impermeability.
Based on the results of the HSG, it becomes possible to establish not only the presence of a lumen in the fallopian tubes, but also the identification of such pathologies as: polyps in the uterine body, uterine, hydrosalpinx, exerting pressure on the outside of the tube, or adhesions in the uterus itself.
Even a successfully performed procedure can sometimes mislead specialists. Studies that were carried out in order to identify the ability to qualitatively detect abnormalities in the condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes are 65%, and the specificity is 80%, which means identifying a certain disease from the probable ones. To examine the state of the uterine body, hysteroscopy is prescribed as an additional diagnosis.

Pregnancy after the study
 Currently available medical information indicates that hysterosalpingography can actually increase a woman's chances of a long-awaited conception, even in those episodes when an oily contrast fluid is used for the purpose of the procedure.
Currently available medical information indicates that hysterosalpingography can actually increase a woman's chances of a long-awaited conception, even in those episodes when an oily contrast fluid is used for the purpose of the procedure.
No one can say about the specific reasons for such an effect of HSG on the possibility of pregnancy.
If you believe the existing assumptions of gynecologists, then the interaction of the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ with a contrast solution containing oils increases its ability to support the formation of an embryo in the initial trimesters of gestation.
Doctors do not have a definite scientific assumption for what reason conception occurs after the HSG. Medical evidence also confirms that this manipulation actually increases the percentage of a woman's ability to become pregnant. In particular, this is often done in situations where the procedure is performed with the inclusion of oils in the contrast fluid.
Therefore, any after the HSG may indicate not only the stress to which the woman was subjected, but also a probable pregnancy, which must be verified without fail.
Cost of the procedure
With regards to the price of conducting an HSG analysis of the fallopian tubes, it is always associated with the method being carried out. In every institution that is on the balance of the state, any event of this kind will be completely unpaid.
In private clinics and medical centers, the cost of an x-ray - the examination may be in the area from 1500 to 5000 rubles. , and on the ECHO-HSG - from 5000 to 8000 rubles . There is also a variation in prices depending on the classification of this analysis.
The maximum cost includes other services:
- specialist advice;
- implementation of the study with painkillers (anesthesia);
- participation of the spouse in the analysis.
Hysterosalpingography is a method of hardware examination in gynecology. Using this technique, doctors determine the condition of the fallopian tubes, their morphological and anatomical features. The main purpose of the study is to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Hysterosalpingography - what is it?
Having seen a record in the direction issued by the doctor: HSG of the fallopian tubes, most patients have no idea what this procedure is. This technique involves the study of the tubes of the uterus and its appendages. The main parameter that doctors examine during this procedure is the patency of the uterine tubes. This factor is of great importance for the successful and bearing of the child. The method is often used to diagnose infertility in women with a long-term absence of pregnancy with its active planning.
What does hysterosalpingography show?
Hysterosalpingography of the fallopian tubes allows doctors to assess the state of one of the most important parts of the reproductive system from the inside. Directly in the fallopian tubes, a meeting of male and female germ cells occurs, therefore, complete or partial obstruction of patency becomes an obstacle to normal conception.
In addition to pathologies of the fallopian tubes, gynecologists use hysterosalpingography to establish a number of other gynecological diseases:
- pathology of the uterus - polyps, deformities, endometriosis,;
- adhesions of the fallopian tubes;
- cysts of the reproductive system;
- tumor-like processes in the uterus and its appendages (including malignant ones).

Hysteroscopy and hysterosalpingography - what's the difference?
The technique of hysterosalpingography is based on the study of the fallopian tubes and the uterine cavity using an X-ray machine. The doctor introduces a special contrast agent into the patient's reproductive system, which helps to better structure the tissues. During the procedure, specialists take several pictures, which are then used to describe and diagnose possible pathologies of the reproductive system.
Hysteroscopy is a simple examination of the uterine cavity using a special optical device. This method cannot be used to obtain information about the condition of the fallopian tubes; it is impossible to visualize them using a hysteroscope. The main purpose of the method is to assess the state of the uterine cavity, endometrium.
The method is used to detect the following pathologies of the uterus:
- polyps of the uterine cavity;
- cystic formations;
- inflammation of the endometrium.
Hysterosalpingography - indications
A fallopian tube test (HSG) can only be carried out with the direction of a doctor. The specialist decides on the need for research, analyzing the clinical picture, the patient's complaints. Often, the procedure is included in the list of examinations when diagnosing the cause of a prolonged absence of pregnancy.
In addition, hysterosalpingography is prescribed by a gynecologist if there are suspicions of a number of pathologies, possible anomalies in the development of the reproductive organ:
- violation of the anatomy of the uterus and appendages (, tortuous fallopian tubes);
- fibroids of the reproductive system;
- adhesions of the fallopian tubes;
- cystic formations;
- polyps.
Hysterosalpingography - contraindications
Due to the presence of a number of contraindications, doctors are not always able to perform HSG: the patency of the fallopian tubes in this case remains in question. Before prescribing an examination procedure, the doctor carefully examines the patient's condition, her medical history, takes into account the presence of other pathologies and inflammatory processes in the woman's body.
Hysterosalpingography is not performed in the following cases:
- the period of pregnancy (especially short terms);
- allergic reactions to a contrast agent (allergic tests for iodine-containing substances are preliminarily carried out);
- uterine bleeding in history;
- inflammatory processes in the body, in the area of the reproductive system and small pelvis;
- period of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- hyperthyroidism;
- thrombophlebitis;
- tumors and cysts in the uterus and appendages;
- viral and bacterial infections in the body.

HSG of the fallopian tubes - preparation for the procedure
Preparation for HSG of the fallopian tubes should begin 7 days before the study. From this moment on, a woman needs to cancel all douching, the use of intimate hygiene products, vaginal creams, and suppositories. Three days before the scheduled procedure, it is necessary to exclude sexual intercourse. The procedure is performed on an empty stomach. Before the HSG, a woman must undergo a series of examinations. The list of them in different clinics may vary.
In most cases, before a hysterosalpingography is performed, preparation for the procedure involves the delivery of the following tests:
- blood analysis;
- testing for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis;
- Analysis of urine;
- on the flora of the vagina;
- cytological scraping of the cervix.
On what day do the HSG of the fallopian tubes?
For women who are to undergo hysterosalpingography, on which day of the cycle to do it, the gynecologist tells. Directly he appoints the time and day of the procedure. The timing of its implementation is determined by the type of pathology. However, in most cases, doctors believe that the best time for research is the period from the beginning of the cycle (after menstruation) to ovulation. So, for women with a menstrual cycle of 28 days, the optimal time for examination is 6–12 days after menstruation. If there is evidence, doctors conduct an urgent examination on any day, except for the period of menstruation.
Hysterosalpingography - what to bring?
Hysterosalpingography, HSG, does not require a woman to have special devices or things. All you need to take with you is a diaper or a large towel. Some doctors recommend grabbing sanitary pads. They are necessary, because after the procedure, abundant vaginal discharge is not uncommon. Everything else will be given to the patient at the clinic where the examination procedure will be carried out.
Hysterosalpingography - does it hurt?
The main question of women who are to be examined for the first time concerns whether it hurts to do hysterosalpingography. In most cases, the manipulation is performed without the use of anesthesia. In this regard, patients may note some discomfort:
- soreness in the lower abdomen;
- light sips in the groin, as during menstruation;
- discomfort in the pelvic area.
To exclude this, some medical institutions perform the procedure under local anesthesia. In some cases, the patient may be asked to take an antispasmodic drug. It helps to reduce tension and contractility of muscles, reduce pain. Women who are very worried about the course of the procedure are given a sedative the day before.

How is hysterosalpingography performed?
When receiving a referral for an examination, a woman wants to get acquainted with the algorithm of the procedure. How the HSG of the fallopian tubes is done, how long the manipulation lasts, whether the pain is strong - the answers to these questions will have to be given to the doctor who sends the woman for examination.
In a conversation with a patient, doctors pay special attention to important preparation rules:
- On the eve of the study, it is recommended to do an enema to completely cleanse the intestines.
- On the day of the study, it is forbidden to eat.
- 1.5 hours before the examination, you can drink a glass of water without gas.
- If hysterosalpingography is performed using ultrasound, the woman, on the contrary, will have to drink a lot of fluid to fill the bladder.
X-ray hysterosalpingography
HSG X-ray of the fallopian tubes is one of the first methods for their examination. Directly with its help, gynecologists for a long time established the condition of the fallopian tubes, the uterine cavity, and diagnosed tubal infertility. The method consists in introducing a special solution into the uterine cavity, which fills the main organ of the reproductive system and gradually penetrates into the tubes. Doctors receive the most detailed pictures, evaluate the body from the inside.
The algorithm boils down to the following:
- The patient is located in the gynecological chair.
- The doctor installs mirrors, cleans the vaginal cavity with sterile swabs.
- A special cannula is inserted into the cervical canal, through which a contrast agent is supplied.
- The mirrors are removed and the uterine cavity is filled with contrast through a special catheter for hysterosalpingography.
- After that, the woman is offered to lie down on a special table, over which the X-ray machine is located.
- The doctor takes pictures at a certain interval, which then evaluates the process of moving the substance through the fallopian tubes.
Ultrasound hysterosalpingography
Ultrasound, or as it is also called, ECHO HSG of the fallopian tubes involves the study of the reproductive system using ultrasound. The principle of the study itself is similar to that discussed above, however, saline is used instead of a contrast solution. On the monitor screen of the ultrasound machine, the doctor manages to visualize the fallopian tubes and the injected solution. If it reaches them and penetrates into the abdominal cavity, the fallopian tubes are passable, there are no pathologies. Otherwise, the doctor in the conclusion indicates the degree of damage, the nature of the changes.
Hysterosalpingography - normal
After the HSG procedure of the fallopian tubes is carried out, the doctor carefully examines the information received. In conclusion, not only the degree of patency is indicated, but also the main parameters of the fallopian tubes. The documents issued to the woman are accompanied by several photographs, which clearly show possible violations. If necessary, the entire course of the procedure is recorded on disk.
In the conclusion of a normal hysterosalpingography, the following information is indicated:
- the uterine cavity has the shape of an isosceles triangle with a base of 4 cm;
- the fallopian tubes are contrasted on both sides;
- ampullary fallopian tubes within normal limits;
- the contrast agent enters the abdominal cavity.
HSG of the fallopian tubes - consequences after the procedure
With the correct, competent conduct of the HSG of the fallopian tubes, the consequences of the procedure for the woman's body are practically excluded. Minor discomfort, reminiscent of pain on the eve of menstruation, together with mild pink discharge, is a variant of the norm. After 2-3 days from the moment of the examination, they completely disappear.
Of great concern to doctors are the possible complications of HSG. Chief among them are allergic reactions to the contrast agent. In addition, the use of a large volume of contrast can lead to the fact that it begins to penetrate into the capillaries, lymphatic vessels, and also into the venous network of the reproductive organ. Excessive administration of fluid can provoke a rupture of the fallopian tube, which requires emergency medical attention.
Pregnancy after HSG of the fallopian tubes
Doctors forbid planning pregnancy after hysterosalpingography in the cycle following the procedure. This is due to the possible negative effect of contrast and X-rays on the reproductive system of a woman. In the case of HSG using ultrasound, these restrictions do not exist.
In general, women after hysterosalpingography, in the absence of impaired patency of the fallopian tubes, can freely plan conception. When, during the course of the study, adhesions and other formations that violate, doctors prescribe complex treatment.
Many women are wondering what HSG and HSS are, how HSS and HSG of the fallopian tubes are done, how informative and safe this procedure is.
Hysterosalpingography and ultrasonic hysterosalpingoscopy are quite often used in gynecological practice. They allow you to safely check the patency and the presence of deformations of the internal female genital organs, as well as to detect morphological pathology. These procedures are highly informative and have a low incidence of side effects.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
What is hysterosalpingography? HSG is such a research method that allows you to carefully examine the inner surface of the uterus and fallopian tubes. It gives maximum information in case of congenital or acquired diseases, which are accompanied by a change in the structure of these organs. For this, a series of x-rays is taken.
HSG is prescribed for suspected of the following diseases and pathologies:
- congenital anomalies in the development of internal female genital organs;
- violation of the patency of the pipes after inflammatory processes, an abortion;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- for diagnosing tubal infertility in a patient after exclusion of hormonal causes (including before IVF);
- specific inflammatory processes (tuberculosis, syphilis);
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- a history of ectopic pregnancies;
- spontaneous abortion at any stage of pregnancy;
- pathology of previous births.
Usually, HSG X-ray or hysteroscopy is performed in patients who have already undergone a complex preliminary examination (OAC, OAM, biochemical blood parameters, ultrasound of the pelvic cavity organs).
Test contraindications
HSG during pregnancy in gynecology is strictly prohibited. There is strong evidence of the negative effects of contrast, as well as x-ray radiation on the fetus. Therefore, the only approved way to diagnose pathology during this physiological state remains a standard ultrasound of the fallopian tubes. Also, HSG should not be performed during lactation.
Also, an absolute contraindication to the study is the presence of any allergic reaction to drugs that are used as a contrast. Many guidelines also strongly recommend that a hypersensitivity test be performed before initiating HSG.
Research is also prohibited under a number of conditions:
- inflammatory processes of the genital organs of the patient;
- the presence of functional insufficiency of the kidneys or liver;
- decompensated cardiovascular diseases (ischemic disease, congenital malformations);
- any form of uterine bleeding;
- hormonal imbalances associated with thyroid disease;
- increased tendency to form blood clots (thrombophilia, thrombophlebitis).
Relative contraindications to HSG of the fallopian tubes include inflammatory changes in general blood tests (leukocytosis, increased ESR, an increase in the number of neutrophils) and urine, bacteriological examination of a vaginal smear.
Ultrasonic hysterosalpingoscopy (USGSS)
Ultrasonic hysterosalpingoscopy is actually a transvaginal ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs with the introduction of glucose, furacilin or saline into the lumen of the uterus. Ultrasound hysteroscopy provides a dynamic image of the spread of fluid in the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes.
This method has a number of advantages over HSG. Ultrasonic hysterosalpingoscopy does not require the introduction of contrast, which eliminates the possibility of allergic reactions, and also reduces the list of contraindications. Also, this method does not expose the patient's body to X-ray exposure. With ECHO HSG of the fallopian tubes, complaints of pain and a feeling of heaviness are less common.
Ultrasound hysterosalpingography, with such a large number of advantages, also has its disadvantages. It visualizes the organ cavity worse, which reduces the information content of diagnostics. The quality of the results depends on the qualifications of the diagnostician, which, if there are errors, has negative consequences in the future.
Preparation for the study
Many patients are concerned about the question of how to prepare for the HSG and USGSS so that the results of the study are as informative as possible. After the appointment of the procedure, all of them are carefully informed about this by the attending physician.

Contrast of the uterus and fallopian tubes
Preparation for HSG of the fallopian tubes and hysterosalpingoscopy consists of several important steps. First, the gynecologist needs to conduct a general examination of the state of the main functional systems of the body. Additionally, the patient is tested for some common infectious diseases (AIDS, syphilis, gonorrhea). On the evening of the day before the study, it is also recommended to conduct a cleansing enema to remove stool from the intestines.
The study is carried out on the 5-10th day of the menstrual cycle. This allows, on the one hand, to almost completely exclude pregnancy in the patient, and on the other hand, a thinner endometrium contributes to a lesser intensity of discomfort during the procedure and better visualization of the organs.
On the day of the HSG or ultrasound for patency of the fallopian tubes, it is necessary to thoroughly toilet the patient's external genital organs, as well as shave her pubic hair, as they may interfere with the study.
The HSG procedure in gynecology involves emptying the patient's bladder immediately before the start of the study. It is also necessary to remove all metal jewelry and clothing in the genital area and pelvis. Hysteroscopy, on the contrary, requires the patient to have a full bladder before the examination.
Research methodology
X-ray examination of pipes for patency is carried out in a special room. The patient takes a seat on a standard table for gynecological interventions. Both HSG and ultrasound of the patency of the fallopian tubes begin with an external examination by a specialist of the woman's external genitalia, vagina and cervix using a gynecological speculum. After that, an antiseptic treatment is carried out and a catheter is inserted into the cervical canal, through which a contrast agent is injected.

The introduction of saline into the uterine cavity and USGSS
The first picture is taken after the introduction of 2-3 ml of contrast. After a short period of time, a second portion of the substance is supplied, which contributes to its penetration into the lumen of the fallopian tubes. It is at this moment that the second picture is taken. With normal tubal patency, some amount of contrast enters the abdominal cavity. If necessary, a third shot is taken after 20-30 minutes.
The use of drugs during the procedure
HSG is considered an almost painless procedure, as is ultrasonic hysterosalpingoscopy. Therefore, anesthesia is used only for severe pain in a very small proportion of patients.
In some clinics, antispasmodics (drotaverine, papaverine) are additionally administered before the study, which allows you to relax the cervix and avoid problems with the introduction of the catheter into the uterine cavity.
Side effects during HSG
Checking the patency of the fallopian tubes with the help of the introduction of contrast may be accompanied by the development of side effects, although in general the procedure is considered absolutely safe. About a third of patients note the presence of discomfort in the abdomen, which sometimes turns into pulling or aching pain.
The most dangerous complication of the procedure is the development of local and general allergic reactions of varying severity. Cases of anaphylactic shock with systemic hemodynamic disturbances are described. Therefore, this procedure is approached by medical personnel with special attention and caution.
If the methodology of the study is violated, traumatic damage to the uterine mucosa by the catheter is not excluded, which is clinically manifested by bleeding from the vagina.
Research results
Hysteroscopy allows for a thorough examination of the uterine cavity and fallopian (fallopian) tubes. The radiologist receives high-quality images of the anatomical structure of the internal genital organs of the patient. They can be used to visualize signs of congenital malformations, the consequences of inflammatory processes, the presence of tumors. It is impossible to establish the type of oncological process with hysterosalpingography, therefore, if it is detected, then a biopsy with a cytological examination is usually performed. Ultrasonic hysterosalpingoscopy also provides information about the condition of the walls of the uterus, the presence of pathology in the myometrium.
Hysterosalpingography remains the leading and simple method for diagnosing the causes of tubal infertility and anomalies in the development of internal genital organs in women. Along with it, ultrasonic hysteroscopy is performed, which is characterized by less information content and high subjectivity of the results, but has fewer contraindications.
A transcript of the results is usually sent to the attending gynecologist or issued to the patient immediately after the study. They not only help to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes by ultrasound, but also determine the further tactics of diagnosing and treating the patient.