What is necrotizing angina? Causes, symptoms and treatment of necrotic tonsillitis (Simanovsky-Vincent) Treatment of purulent-necrotic tonsillitis
Necrotic angina or, as it is also called, ulcerative necrotic angina, is an acute pathology caused by exposure to conditionally pathological microflora present in the oral cavity. Conditionally pathological microflora is called, which is present in the body in a small amount and does not affect it in any way, at least as long as it is healthy. As soon as the body weakens, this microflora begins active reproduction. In most cases, ulcerative angina is caused by microorganisms such as spirochete and fusiform bacillus. Due to the fact that the pathology is of a tonsillar nature, in medicine the disease is referred to as tonsillitis.
Essence of pathology
Most often, the progression of this microflora begins with a strong depletion of the body and protein deficiency. This one is often referred to as the "trench" as it often appeared in World War II soldiers due to their frequent malnutrition. Diseases such as leukemia, radiation sickness, hypovitaminosis, etc. can also contribute to the progression of conditionally pathological microflora.
 In normal cases, the pathology affects only one tonsil, but there have been cases when necrotizing tonsillitis was bilateral. Over time, in the absence of proper treatment, the disease progresses greatly and ulcerative formations pass into the area of \u200b\u200bthe sky and pharyngeal arch. The mucous membranes of the cheeks, gums and other parts of the oral cavity and pharynx are affected. Despite the fact that this pathology is not considered contagious, the epidemiological nature of the disease is sometimes noted.
In normal cases, the pathology affects only one tonsil, but there have been cases when necrotizing tonsillitis was bilateral. Over time, in the absence of proper treatment, the disease progresses greatly and ulcerative formations pass into the area of \u200b\u200bthe sky and pharyngeal arch. The mucous membranes of the cheeks, gums and other parts of the oral cavity and pharynx are affected. Despite the fact that this pathology is not considered contagious, the epidemiological nature of the disease is sometimes noted.
If the disease is detected in time and the correct treatment is started, then in almost all cases a cure occurs. With proper and timely therapy, complete recovery occurs within 14 days. But if the immune system of a sick person is weakened, the duration of the disease increases to several months.
Back to index
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Necrotic angina can be primary and secondary. It should be noted that in the progressive processes of the disease, in addition to saprophytes, various coccal fungi also participate. These include streptococci and staphylococci.
The causes of the appearance of primary necrotic angina include suppuration, pyorrhea in the oral cavity. Carious teeth can contribute to the appearance of the disease. Diseases such as diphtheria, scarlet fever, leukemia, tularemia, etc. contribute to the appearance of secondary ulcerative angina.
 The disease begins its progression imperceptibly for the sick person. At first, there is some awkwardness in the process of swallowing and a feeling of discomfort in the throat. Over time, after the attachment of coccal fungi to the pathological process, severe pain appears. Patients have a feeling of a foreign body in the throat, and there is also an unpleasant smell of pus from the mouth. If a pharyngoscopy is performed, the presence of a grayish-yellow coating is noted on the tonsils, which is easily removed. When you try to open the exudate, the ulcer opens and bleeds.
The disease begins its progression imperceptibly for the sick person. At first, there is some awkwardness in the process of swallowing and a feeling of discomfort in the throat. Over time, after the attachment of coccal fungi to the pathological process, severe pain appears. Patients have a feeling of a foreign body in the throat, and there is also an unpleasant smell of pus from the mouth. If a pharyngoscopy is performed, the presence of a grayish-yellow coating is noted on the tonsils, which is easily removed. When you try to open the exudate, the ulcer opens and bleeds.
Necrotic angina is characterized by the fact that the patient's body temperature is normal and does not rise. At the same time, other local changes in the body appear. However, sometimes there are cases when ulcerative tonsillitis begins with hyperthermia and chills. The main symptoms of the disease include the following signs:
- Hyperemia of the tonsils affected by tonsillitis.
- Profuse salivation.
- Increased lymph.
- moderate leukocytosis.
- body intoxication.
Back to index
Diagnosis and treatment of necrotic angina
 The diagnosis is determined by the attending ENT doctor. The specialist establishes the diagnosis, based on the examination of the patient and the testimony of studies of the biomaterial taken from the surface of the affected tonsil. Some tests require a swab of the purulent coating and mucous membrane of the tonsil. The following tests are carried out:
The diagnosis is determined by the attending ENT doctor. The specialist establishes the diagnosis, based on the examination of the patient and the testimony of studies of the biomaterial taken from the surface of the affected tonsil. Some tests require a swab of the purulent coating and mucous membrane of the tonsil. The following tests are carried out:
- Identification of an infectious agent, its sensitivity to drugs and its resistance. For this, planting on the nutritional value of the flora is carried out.
- To detect hemolytic streptococcus type beta, an antigenic test is performed.
- To determine the variety of microflora, PCR analysis of a DNA fragment is performed.
Analyzes will help to exclude the syphilis and tuberculous nature of ulcers. The development of a malignant tumor, diphtheria of the throat and lacunar tonsillitis are also excluded.
Treatment of necrotizing tonsillitis is carried out under the supervision of a physician. Therapy uses tools such as:
- Hydrogen peroxide.
- Furacilin.
- Iodine tincture.
- Silver nitrate.
- Glycerin solution of novarsenol.
- potassium chloride.
- Potassium permanganate.
Tonsils must be processed every day several times. If there is no effect when using these drugs, doctors prescribe injections of penicillin group drugs.
Necrotic angina is the most severe form of inflammation of the palatine tonsils, caused by saprophytes of the oral cavity, primarily spirochetes and fusiform rods. A feature of this form of angina is the rapidly developing necrotic lesion of the tonsils, which threatens to disrupt the structural and functional integrity of the organ, as well as the destruction of the oropharyngeal lymphoepithelial ring of Waldeyer-Pirogov, which is the first outpost on the path of penetration of pathogens of infectious diseases into the human body.
Features of the development of necrotic tonsillitis
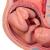
Necrotizing tonsillitis, as a rule, develops in people with reduced immunity and a lack of vitamins C and B, AIDS, cachexia, and symptoms of general poisoning of the body. For the course, necrotizing against the background of inflammation is typical. Necrotic angina, the photo of which is presented below, is characterized by unilateral (rarely bilateral) lesions of the tonsils. A grayish-yellow coating appears on them, under which bleeding ulcers appear.
Manifestation of necrotic angina
Ulceration can spread beyond the tonsils to the soft palate, gums, back of the pharynx, descend into the vestibular larynx, affect the Eustachian tube. In some cases, the necrotic process can cover the underlying tissues up to the periosteum. That is why it is so important to stop necrotizing in time.
Reasons for the development of necrotic tonsillitis
The causative agent of necrotic sore throat is a symbiosis of saprophytes of the human oral cavity - spirochetes and fusiform rods. These are opportunistic pathogens, which are found in large numbers in healthy people. Thus, necrotic tonsillitis refers to bacterial tonsillitis.
In order for the conditionally pathogenic spirochetes and spindle-shaped rods to pass into a pathogenic form, a number of conditions must be met.
So, the main causes of necrotic angina are:
- long course of concomitant infection (scarlet fever, diphtheria, tularemia);
- the presence of foci of chronic infection (ulcerative lesions of the gums and oral mucosa, carious teeth, periodontal disease);
- immunodeficiency of various origins;
- purulent-inflammatory;
- violation of the rules of oral hygiene;
- complication .
In addition, ulcerative necrotic angina can be a complication of leukemia. The development of most complications is associated with childhood, a period when the body's defense system is not yet fully formed.
Symptoms of necrotizing sore throat in adults and children
Purulent-necrotic angina is characterized by a satisfactory condition of the patient. The manifestation is localized in the oral cavity: putrid odor, excessive work of the salivary glands, pain in the process of swallowing and chewing. stays around 37-38°C.
Necrotic angina can be primary and secondary. In addition to the main pathogens, and play an important role in the development of the disease. manifests with difficulty in swallowing, feelings of a foreign body in the throat. Concomitant infection provides pain syndrome. The defeat of the tonsils is characterized by the appearance of a grayish-yellow plaque, with the separation of which bleeding necrotic ulcers are opened.
Symptoms of necrotizing sore throat include the following manifestations:
- increased salivation;
- lymphadenitis;
- general intoxication of the body - weakness, headache, nausea;
- a strong cough, as a result of which plaque is separated from the tonsils;
The main manifestation of the disease, which determines its name, is necrosis. This is the death of body cells, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process. Unlike programmed cell death (apoptosis), necrosis is uncontrolled. Therefore, the immune system tries to protect the necrotic areas from healthy body tissues by sending white blood cells there, which devour dead tissues and bacterial cells. As a result of this, ice is formed visible on the surface of the tonsils. If the layer on the tonsils is colored green, this indicates the presence of anaerobic bacteria in the exudate, which corrects the selection of drugs for drug therapy.
However, at the beginning of the disease, the symptoms of necrotic tonsillitis are superficial. Timely treatment will prevent damage to the lymphoid tissue and prevent the discovery of extensive bleeding and perforation of the soft palate.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of necrotic sore throat begins with an examination and history taking. As a rule, the disease is accompanied by febrile fever (variants with normal and subfebrile temperature are also possible) and constricting sore throat. The clinical picture for this disease is very characteristic, which allows you to accurately diagnose.
With pharyngoscopy, the doctor usually reveals a typical erosion on one of the palatine glands with a characteristic plaque, which, when removed, opens a bleeding wound. For any of the sore throats, painful sensations during swallowing are characteristic. It is also necessary to monitor the patient's temperature chart.
From the first day of treatment, the patient must pass a general blood test, in which, with the diagnosis of "purulent-necrotic tonsillitis", the level of leukocytes will be increased, and the ESR will also be increased.
With the help of bacteriological examination by taking a smear from the affected tonsils and sowing it on a nutrient medium, the state of the microflora of the patient's oral cavity is determined. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of grown colonies is possible. Bacteriological research is also used to determine the antibiotic to which pathogens will be most sensitive. The bacteria themselves can be seen using electron microscopy. Using PCR diagnostics, it is possible to confirm the presence of spirochetes and spindle-shaped rods in a smear by detecting fragments of their genetic material.
With the help of a rapid test for antigens, beta-hemolytic streptococcus is excluded.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with diphtheria, tularemia, scarlet fever, tuberculosis, tumor process of the oropharynx, oncological diseases of the blood and viral tonsillitis.
Treatment of necrotic sore throat - medication, folk
Treatment of necrotic tonsillitis should be carried out in a hospital under the supervision of an infectious disease specialist and an ENT doctor. Since the causative agents of the disease are bacteria, the main ones will be. With antibiotic therapy, it is important to strictly observe the terms of treatment and dosage of drugs. Otherwise, complications of the disease and a complex of unpleasant side effects are possible. The main antibiotic for angina is traditionally penicillin.
For treatment apply:
- Benzylpenicillin;
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin.
Often use broader spectrum antibiotics - cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Ceftriax, Cephaloridine).
If you are allergic to these groups of drugs, you can use macrolides, which do not have many unpleasant side effects. When using them, there is no toxic effect on the nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract. This fact is associated with the widespread use of macrolides in children. In addition, this group of drugs, in addition to a strong bacteriostatic effect, has an immunomodulatory effect, and also has a high affinity for lymphoid tissue.
Macrolide drugs include:
- Erythromycin;
- Leukomycin;
- Azithromycin.
For local treatment of necrotic sore throat, solutions with an antiseptic effect are used.
The affected tonsils must be treated several times a day and systematically gargle with one of the following solutions:
- Furatsilin alcohol.
- Miramistin.
Treatment of necrotizing ulcerative angina also often involves physical therapy. In particular, irradiation of the oral part of the pharynx with short-wavelength ultraviolet rays is often used.
Important! This method is applicable only after the acute phase has passed. Irradiation has a thermal effect on the tissues of the tonsils, increasing the rate of blood flow in them. Along with this, it is possible to carry out inhalations using solutions of Lysozyme and Dioxidine.
Remember that the treatment of purulent-necrotic sore throat by folk methods is impossible. The disease, also with a mild course, requires medical treatment with the use of strong antibiotics. Otherwise, the patient is threatened with complications from the cardiovascular system (bacterial endocarditis and mitral insufficiency), renal (infectious glomerulonephritis) and others. Folk remedies for sore throats can only be an addition to medicines, but not a replacement for them. In addition, folk remedies have a symptomatic effect, that is, they do not have an effect on the cause, the causative agent of the disease.
The main ones against the disease in question include:
- lubrication of the affected areas with aloe juice, onion or garlic;
- gargling with a solution of sea salt or medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, St. John's wort);
- the use of home multivitamin complexes and bee products.
Features of the treatment of necrotic tonsillitis in children
In early childhood, the incidence of tonsillitis of this type is very low. This is due to the absence of many causes of the development of the disease, for example, carious process in the teeth and acquired immunodeficiency. However, the protective system of the child's body can still malfunction, in which case necrotic tonsillitis may develop.
The disease in children is faster and more severe than in adults. The symptoms are similar, but the manifestations develop more rapidly. If the temperature can be maintained within the subfebrile range, only local therapy from antimicrobial and antiseptic agents is prescribed. In case of complications, antibiotics should be used. Preferably, drugs of the macrolide group will be preferable due to their low toxicity.
Treatment of necrotic sore throat in pregnant women
The danger of the disease in pregnant women is associated with the risk of developing complications that could affect the health of the fetus. In the event of purulent tonsillitis in women during pregnancy, it is necessary that its treatment, in addition to the infectious disease specialist and ENT doctor, is also controlled by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Also, attention should be paid to the strict dosage of drugs and the exclusion from their number of those that can adversely affect the fetus. If it is the woman's immune system that allows her to cope with the disease on her own, then it is better to do without antibacterial agents altogether, limiting herself to local therapy and folk remedies.
Complications and consequences of necrotic angina
The disease in question most often develops against a background of weakened immunity, therefore, there is a high probability of joining a concomitant primary infection. With insufficient, incorrect or untimely treatment, the development of local and generalized complications is possible.
Local complications include damage to the oral cavity. Necrotizing tissue of the palatine tonsil can gradually move into the area of the soft palate, which, ultimately, can lead to its perforation. It is also possible the occurrence of abscesses, phlegmonous manifestations, hemorrhages and pyorrhea.
Generalized complications are much more dangerous. Even if they are stopped and stopped in time, the possible consequences can haunt a person for the rest of his life.
can cause:
- rheumatic damage to the heart tissue;
- blood poisoning (sepsis);
- glomerular dysfunction.
All complications from this group can develop into chronic diseases. In this regard, the question of the timely diagnosis of tonsillitis and the adoption of adequate measures for its treatment becomes the first place.
Forecast and prevention of necrotic sore throat
The prognosis of tonsillitis with timely treatment and the absence of allergy to antibiotics is favorable. Necrotizing tonsillitis is well treated, and in the absence of complications will not leave any consequences. Specific rehabilitation is also not required.
Tonsillitis, like any other disease, is easier to prevent than to cure. In matters of prevention, an important role is played by the general strengthening of immunity, the lack of contact with people in the acute period of the disease (the first week of the course of the disease). Patients with the diagnoses under consideration should be isolated. In places of their stay, carry out daily wet cleaning with a disinfectant solution. Provide personal utensils.
Choose a rubric Adenoids Angina Uncategorized Wet cough Wet cough In children Sinusitis Cough Cough in children Laryngitis ENT Diseases Folk methods of treating Sinusitis Folk remedies for cough Folk remedies for the common cold Runny nose Runny nose in pregnant Runny nose in adults Runny nose in children Sinusitis Cough Treatments Cold Treatments Symptoms of Sinusitis Cough Syrups Dry Cough Dry Cough in Children Temperature Tonsillitis Tracheitis Pharyngitis
- Runny nose
- Runny nose in children
- Folk remedies for the common cold
- Runny nose in pregnant women
- Runny nose in adults
- Runny nose treatments
- Cough
- Cough in children
- Dry cough in children
- Wet cough in children
- Dry cough
- Moist cough
- Cough in children
- Drug Overview
- Sinusitis
- Alternative methods of treatment of sinusitis
- Symptoms of Sinusitis
- Treatments for sinusitis
- ENT Diseases
- Pharyngitis
- Tracheitis
- Angina
- Laryngitis
- Tonsillitis
The main causative agents of the disease are spindle-shaped bacteria and spirochetes. Less commonly, pathology manifests itself due to exposure to the mucous membranes of such pathogenic agents as staphylococci and streptococci. Such microorganisms constantly live in the human oral cavity, while not causing the development of the disease. Pathology begins to manifest itself in the case of a decrease in the protective function of the body. The provoking factors due to which ulcerative necrotic (or gangrenous) tonsillitis develops, experts call the following conditions:
- deficiency of minerals and vitamins in the diet;
- inflammation of the throat with a chronic course (tonsillitis);
- cachexia;
- weakening of the immune system;
- an excess of vitamins B and C;
- foci of infection in the gastrointestinal tract;
- dystrophy;
- recurrent pharyngitis;
- allergic reactions;
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis;
- periodontal disease;
- non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene;
- the presence of purulent discharge in the pharynx.
The necrotic form of angina quite often becomes a complication of some serious diseases. Among them are oncological processes of the blood (for example, acute leukemia), infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, tularemia). Necrosis of the tonsils when the pathological process is neglected extends to the tissues of the larynx, sometimes the tongue, periosteum, and soft palate.

Symptoms of necrotic inflammation
Filmy angina has its own characteristic clinical manifestations. The patient will complain of soreness during swallowing. The intensity of this symptom increases in case of secondary infection. Perspiration in the goal is the first sign of the beginning of the development of the pathological process.
For the disease, unilateral damage to the tissues of the tonsils and pharynx is most characteristic. The occurrence of more common structural changes is less common. Patients complain of discomfort in the throat. It is manifested by the sensation of having a coma that cannot be coughed up or swallowed.
The ulcerative membranous form of angina also has nonspecific symptoms. Purulent-necrotic tonsillitis is accompanied by an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes (cervical, occipital, submandibular). Common manifestations of the disease include intoxication syndrome. It includes an increase in body temperature (up to a maximum of 37.5 degrees, but in most cases it is normal), headache, lethargy, decreased performance. An unpleasant (purulent) smell from the mouth, increased salivation (salivation) and dehydration of the body are often observed with angina. Depending on the clinical manifestations, the doctor decides how to treat the patient symptomatically.
During the progression of the disease, plaque forms in the throat and on the tonsils. In this case, the walls of the pharynx and tonsils are covered with a loose film. It is easily separated by mechanical action on it or by coughing. When the plaque is detached from the tissues, a small bleeding ulcer is formed, which has jagged edges.

Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis is essential for adequate therapy. The diagnostic process includes questioning the patient (collection of complaints, anamnesis of the disease), examination and laboratory and instrumental examinations.
After examining the patient visually and with the help of palpation, the doctor determines the enlargement and soreness of the lymph nodes, the presence of yellow or gray plaque on the tonsils (signs of necrosis, or necrosis, of mucosal areas), tongue, and on the walls of the pharynx. At the initial stages of development of the ulcerative type of angina, the changes are superficial.
As the disease progresses, the lesion spreads deep into the tissues of the tonsils, larynx, and tongue.
During a visual examination of the patient's throat, hyperemia (redness) of the tonsils and throat walls is determined.
With a purulent-necrotic type of angina, the following laboratory tests are carried out:
- General clinical analysis of blood.
- Bacterial culture to determine the microflora.
- Antigen test.
- polymerase chain reaction.
- Determination of the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotic drugs.
It is also necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis in order to exclude the development of diphtheria, an oncological process, and lacunar tonsillitis. In addition, it is important to distinguish necrotizing tonsillitis from syphilis, tuberculosis.
In the general blood test, there are changes in the level of leukocytes (increase) and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Rapid antigen analysis is essential for the detection of Beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Polymerase chain reaction allows you to identify the pathogen by particles of nucleic acid - DNA. When sowing, it is possible to determine which drugs are best to treat the patient in order to eliminate the ulcerative-necrotic form of angina.

Treatment of purulent-necrotic tonsillitis
Therapy for ulcerative membranous inflammation of the tonsils includes both systemic and local therapeutic measures. Such combined treatment is necessary to prevent the development of complications of the disease. The diet is also important.
Drug treatment is intended to eliminate the symptoms and the etiological factor. Symptomatic therapy includes taking headache pills (for example, Analgin, Paracetamol, Aspirin). To eliminate the cause of necrotic sore throat, antibiotic drugs are used. The necessary medicines are selected by the attending doctor after bacteriological seeding. Means to which the pathogen is not sensitive should not be used. This is due not only to the lack of effect, but also to the risk of developing microflora resistance to antibiotics.
Groups of drugs that are used to treat necrotizing tonsillitis:
- Macrolides ("Azithromycin", "Midecamycin", "Erythromycin", "Clarithromycin").
- Penicillins ("Phenoxymethylpenicillin", "Benzylpenicillin", "Amoxicillin").
- Cephalosporins ("Cefilaxin", "Ceftriaxone", "Cefuroxime", "Cefepime", "Cefotaxime").
Most often, doctors recommend using drugs from the macrolide group. This is due to high efficiency and minimal effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. The bacteriostatic effect of drugs contributes not only to the elimination of pathogenic microflora, but also to the blockade of the reproduction of individual bacteria that could survive.
For a quick recovery, you need to follow a diet. The diet includes food rich in animal protein. These dishes include:
- poultry meat, as well as beef, rabbit;
- liver;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir, yogurt;
- eggs.
It is good to eat foods rich in vitamins. These include fresh vegetables and fruits. Rose hips, viburnum, cranberries can be used to prepare delicious drinks containing vitamin C.
When treating the necrotic form of angina, dishes that cause irritation of the mucous membrane are excluded from the diet. Is it hot or too cold food. It is not recommended to eat solid food, as it can mechanically damage the affected tissues. The patient should not eat spicy, salty, very spicy foods.

Local treatment
In addition to the use of antibiotic drugs, rinsing, wiping the tonsils with therapeutic solutions are highly effective. Before starting such procedures, it is necessary to remove the film with a spatula from the affected surface. Then it is required to process the formed ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane. To do this, use solutions of such means:
- Hydrogen peroxide.
- potassium chloride.
- "Furacilina".
- Potassium salt of permanganic acid.
Rubbing the tonsils with these medicines should be done up to five times a day. In addition, it is recommended to treat tonsils and affected areas of the pharynx with sores with Lugol's iodine solution, tincture of chlorophyllipt.
For rinsing, as well as for wiping, it is necessary to dilute hydrogen peroxide in the ratio of 2 tablespoons of the product per 200 milliliters of clean boiled water. The medicine with potassium permanganate is prepared in such a way that the concentration of the active substance is 0.1%. In addition, a weak solution of silver nitrate can be used for rinsing.
Also quite effective in local therapy are folk remedies. Decoctions from such medicinal plants are widely used:
- sage;
- oak (bark is used);
- mint;
- viburnum (use both leaves and young branches);
- hypericum;
- chamomile.
To prepare the product, it is necessary to boil them for about 15 minutes in a steam bath. Then the broth should be infused and cool for forty minutes. For medicine, you can take one plant from the list, or several.
Salt solution is considered effective. You can also add a teaspoon of baking soda and a drop of iodine to it. This will enhance the effect of sea salt on pathogenic bacteria and contribute to the rapid onset of the result.
Tonsils can also be treated with juice of vegetables that contain phytoncides. For this purpose, garlic and onion puree is squeezed out, gauze is moistened in the resulting liquid and the tonsils are wiped. Calendula tincture is used to stimulate the healing of ulcerative mucosal defects that bleed.
Also, local treatment includes physiotherapy. To do this, carry out the KUV pharynx. Such an event has a warming effect on the parenchyma of the tonsils. Thanks to this, blood circulation is stimulated, acute inflammation is eliminated and the healing process is accelerated. Physiotherapy also includes ultraphonophoresis with antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs.

Forecast
The disease usually has a favorable prognosis. But this is only subject to all the recommendations of the doctor. The healing process takes from 8 days to two weeks. With a weakened immune system, it is possible to increase the duration of the disease up to several months.
Since necrotizing tonsillitis is a serious disease, treatment should be carried out in a hospital or at home, but under the supervision of a doctor. The disease often causes the development of dangerous complications. To avoid such a situation, the patient should seek help from a specialist at the first signs of a pathological process.
Possible complications: what is the danger of the disease
In case of inadequate treatment, or in case of untimely access to the doctor, the consequences of angina may develop. In this case, complications can be both local and generalized. Local include conditions in which the lesion is determined on adjacent tissues. The second variant of the consequences develops with the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the bloodstream. This entails the occurrence of an inflammatory process in distant organs.
Local complications otolaryngologists include the following conditions:
- necrosis of oral tissues;
- abscess;
- bleeding;
- perforation of the hard palate;
- destruction of the gums;
- phlegmon.
The list of generalized consequences includes:
- rheumatoid fever;
- endocarditis;
- rheumatism;
- myocarditis;
- sepsis;
- pericarditis;
- glomerulonephritis.
The likelihood of developing such severe consequences is high in the case of improperly selected drugs, non-compliance by the patient with the treatment regimen. In case of complications, hospitalization of the patient is necessary. Only adequate therapeutic measures will save the patient from aggravating the pathological process.

Prevention
To prevent the development of ulcerative necrotic angina, you must follow a few simple rules. First of all, timely rehabilitation of all pathological foci of infection is important, this includes the treatment of caries and periodontal disease. Also, for the prevention of angina, it is necessary to exclude hypothermia, contact with carriers of the disease.
Tempering the body and playing sports are good ways to protect yourself from the disease. Such methods help to stimulate the protective reserves of the body. Proper nutrition also helps to strengthen the immune system. In the diet, be sure to include foods high in vitamins. It is necessary to completely exclude alcoholic beverages, smoking cessation.
Ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis is best prevented. Since many patients believe that they have another common cold. Therefore, due attention is not paid to treatment and severe complications occur. Some of them can be fatal (for example, sepsis), especially if the immune system is weakened. Only a specialist is able to save the patient from such consequences.
1 ratings, average: 5,00
out of 5)
Ulcerative-necrotic tonsillitis, or ulcerative-film tonsillitis of Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent, is a non-infectious disease of the larynx caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The microorganisms that provoke it - spirochete and fusiform bacillus - are often constant companions of even a healthy person and live on the mucous membranes of the lips, cheeks and throat, without showing their existence in any way. But under certain circumstances, they are activated, the form of their life changes, and as a result, necrotic tonsillitis occurs. We will talk about the causes of such negative changes, the first signs of the disease, its symptoms and methods of treatment in this article.
Necrotizing angina is often accompanied by an unpleasant smell of rot from the mouth and stomatitis. On examination, the otolaryngologist discovers an enlarged loose tonsil covered with a white coating with a grayish or yellowish tint. If you touch it with a spatula, it easily separates from the tissue of the tonsils, leaving behind a slight bleeding and a recess with jagged edges. The laboratory analysis of the plaque (inoculation on a nutrient medium, antigen test, polymer chain reaction analysis) and the discrepancy between general and local symptoms, namely the patient's able-bodied condition with severe tissue damage, help the doctor to make the final verdict. A general blood test at the same time shows an increased content of leukocytes and an increase in ESR.
Local therapy includes a number of measures aimed at the gradual cleansing of damaged tissues from purulent and mucous plaque, their healing and restoration.
Among the comprehensive measures must be present:

What catarrhal angina looks like can be seen in the photo in this
Mode and diet
Depending on the stage of tonsillitis, the patient may be offered to be treated on an outpatient basis with all preventive precautions (separate dishes, maximum isolation from others, bed rest) or in an infectious diseases hospital. 
A lot of attention will have to be paid to the diet.
Food that can irritate the mucous membranes should be completely excluded from it: too hot or cold, as well as too hard. The patient is advised to give up spicy, salty, spicy foods, replacing them with soft, frayed ones.
How is the treatment of purulent tonsillitis during pregnancy indicated in this
The diet must be saturated with animal protein:
- poultry meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal, beef);
- kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese and dishes from it;
- liver and other offal;
- hard cheese;
- eggs (except cooked soft-boiled - they may contain pathogenic bacteria).
We must not forget about the drinking regime. The patient will benefit from a plentiful drink, consisting of compotes and fruit drinks saturated with vitamins B and C, rosehip broth, freshly squeezed juices, tea with lemon. To replenish the body's vitamin reserves, fruit and vegetable purees, citrus fruits (especially oranges and grapefruits) are perfect.
What medications for sore throat during pregnancy are the most effective, indicated in this
Subject to the fulfillment of all doctor's prescriptions, the prognosis is favorable. The disease can be defeated within 7-20 days, and, as a rule, it does not reach necrosis. For the prevention of ulcerative necrotic angina, it is necessary to adhere to proper nutrition at the stage of recovery after viral and infectious diseases, if necessary, take restorative and immunostimulating drugs, and timely sanitize the oral cavity.
Tonsillitis is an acute disease characterized by pathological changes and inflammation of the palatine tonsils.
Depending on the severity of the disease, doctors distinguish several types of tonsillitis, but ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis is rightfully considered its most dangerous variety.
It is sometimes called Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent tonsillitis.
Ulcerative membranous angina is characterized by mild symptoms:
- there is no high body temperature;
- the patient's health is not critical, satisfactory;
- the patient does not experience severe pain when swallowing.
Often ulcerative-film tonsillitis is accompanied by the appearance of abscess foci on the tonsils (most often only on one of them). Many patients noted the presence of a grayish coating covering the pharynx and root of the tongue.
Causes of the disease

Ulcerative membranous angina appears in a patient due to infection of the body with microbes or viruses. Its causative agents are:
- streptococci;
- adenoviruses;
- staphylococci.
Ulcerative necrotic angina can be transmitted:
- by airborne droplets;
- through poorly processed foods;
- cutlery can also successfully spread the infection;
There are a number of internal factors that can cause such an ailment as ulcerative membranous tonsillitis:
- carious destruction of teeth;
- chronic diseases of the tonsils;
- cystic neoplasms of the gums.
Provocateurs of ulcerative angina are:
- low air temperature, contributing to the rapid hypothermia of the body;
- overwork;
- ulcerative membranous angina can manifest itself as a complication obtained in connection with the progression of another serious disease (for example, influenza).
Many experts in the field of medicine believe that necrotizing ulcerative angina is a seasonal ailment: a person is more likely to get sick with it in the autumn-winter period than in summer.
Symptoms of the disease
Ulcerative membranous angina is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- slight increase in temperature (up to 38 degrees);
- an increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes;
- a palpable feeling of weakness;
- slight pain when swallowing, as well as a sore throat;
- the occurrence of abscesses and white plaque on the palatine tonsils;
- throat redness.
Their manifestation is clearly demonstrated by the photo:

Symptoms of ulcerative-filmous tonsillitis resemble the common cold. Among the differences are the following:
- angina is more difficult to tolerate than the usual SARS;
- the duration of the illness exceeds 7 days.
A patient who has noticed the first signs of ulcerative-filmous tonsillitis should immediately contact a medical institution to draw up a competent strategy to combat the disease.
Diagnosis of acute tonsillitis of the ulcerative type

Ulcerative membranous angina lends itself well to diagnosis. In this case, the doctor uses the following tactics:
- a thorough examination of the throat with medical devices (for example, a pharyngoscope);
- assessment of the patient's complaints, as well as his general condition;
In case of difficulty in making a correct diagnosis, the doctor can take the following measures:
- swabs from the nose and throat;
- laboratory tests for the presence of pathogen cells.
Treatment of the disease

The treatment of a disease such as ulcerative necrotic angina is carried out with the help of medical measures, as well as some of the remedies that traditional medicine offers us. Therapy is prescribed by a doctor, and its intensity is determined by the following factors:
- the patient's condition;
- the severity of the disease.
Treatment includes the following:
- Complete isolation of the patient in order to prevent possible complications (this measure is also taken to avoid the spread of infection and infection of healthy members of society);
- Treatment of such an ailment as ulcerative necrotic angina involves patient compliance with bed rest;
- Careful hygiene of the room in which the sick person is kept:
- room ventilation;
- wet cleaning;
- irradiation of space with ultraviolet light (the measure is not mandatory and is applied only in cases where the opportunity allows);
- Treatment of the disease with the help of traditional medicine:
- gargling with decoctions of medicinal plants:
- chamomile;
- sage;
- eucalyptus.
- compresses;
- wellness baths;
- inhalation.
- gargling with decoctions of medicinal plants:
- Compliance with the diet (the patient is contraindicated in eating food that can injure the palate);
- Treatment involves taking medications:
- antipyretic;
- painkillers;
- antibacterial;
- antibiotic.

If the patient is not given proper treatment, then the likelihood of complications increases, among which the following are most often observed:
- heart disease;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- partial atrophy of the joints;
- local complications:
- otitis;
- mastoiditis.
- swelling of the larynx;
- cellulitis.
Prevention of angina
After the patient has been given treatment, it is necessary to follow measures that help to minimize the possibility of a recurrence of the disease.
Among them are:
- hardening;
- gargling with cold water (its temperature is recommended to be reduced gradually);
- ultraviolet irradiation in order to increase the resistance of immunity to aggressive factors of external influence.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
There are three available methods of preventing viral diseases - following them, you can cheerfully survive the height of the seasonal epidemic. An experienced family doctor Konstantin Zelensky spoke about how to reduce the likelihood of a disease by 90% in the studio of the show “Everything will be kind”.